Biliopancreatic Diversion
Are you tired of trying every fad diet and exercise regimen with no long-term success? If so, you’re not alone. Many individuals struggling with obesity find it challenging to shed those extra pounds and keep them off for good. Thankfully, there is a surgical solution that can provide lasting weight loss results – biliopancreatic diversion. In this blog post, we will explore what biliopancreatic diversion is, how it works, its benefits, the associated risks and complications, who is an ideal candidate for the procedure, and what to expect during recovery. So let’s dive in and discover how biliopancreatic diversion surgery can be your ticket to achieving a healthier weight!
What is Biliopancreatic Diversion?
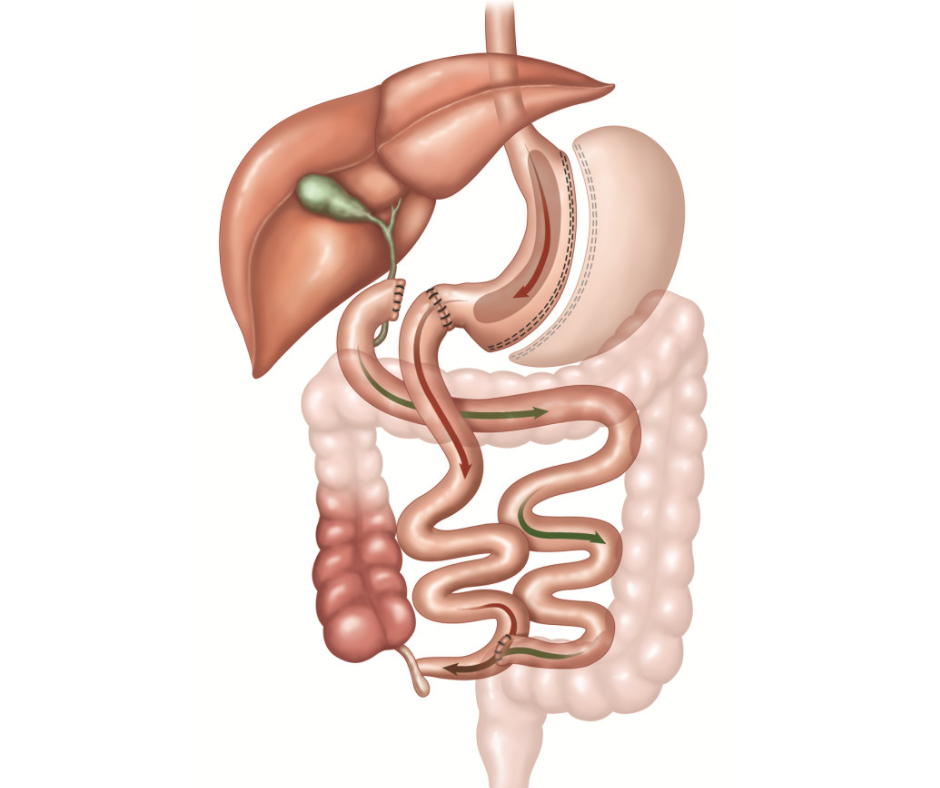
Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD), also known as duodenal switch surgery, is a surgical procedure designed to help individuals struggling with severe obesity achieve significant and long-term weight loss. Unlike other weight loss surgeries that primarily restrict the amount of food intake or limit nutrient absorption, BPD combines both approaches for optimal results.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes changes to both the stomach and small intestine. A portion of the stomach is removed to create a smaller pouch. This limits the amount of food that can be consumed at one time and promotes feelings of fullness sooner.
Next, a section of the small intestine is bypassed by connecting it lower down in the digestive tract. This reduces nutrient absorption while ensuring proper digestion still occurs further along in the intestinal tract.
The combination of these modifications leads to significant weight loss because patients consume fewer calories due to their reduced stomach size and absorb fewer nutrients from their diet.
Biliopancreatic diversion aims not only to help patients lose excess weight but also improve overall health by addressing co-morbidities associated with obesity such as diabetes and hypertension. So if you’ve tried everything else without success, it may be time to consider this effective surgical solution for long-term weight loss!
How Biliopancreatic Diversion Works
Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD) is a surgical procedure that helps individuals achieve long-term weight loss by altering the way their digestive system functions. This procedure is typically recommended for patients with severe obesity who have not been successful with other weight loss methods.
So, how does Biliopancreatic Diversion work? During the surgery, the surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach and then connects it directly to the lower part of the small intestine. By bypassing a significant portion of both the stomach and small intestine, BPD limits both calorie intake and nutrient absorption.
This alteration in digestion leads to weight loss as fewer calories are consumed and absorbed by the body. Additionally, this procedure can also affect hormone levels in a way that reduces hunger and increases feelings of fullness.
It’s important to note that BPD is considered more complex than other weight loss surgeries like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. It requires careful consideration from both patients and medical professionals due to its potential risks and complications. Therefore, thorough evaluation and consultation with an experienced surgeon are necessary before deciding on BPD as a treatment option for obesity.
Biliopancreatic diversion works by altering digestion through creating a smaller stomach pouch connected directly to a lower portion of the small intestine. This results in reduced calorie intake, limited nutrient absorption, decreased hunger levels, increased satiety feelings leading ultimately to long-term weight loss
Benefits of Biliopancreatic Diversion
Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD) surgery is gaining recognition as an effective solution for long-term weight loss. But what exactly are the benefits of this procedure?
1. Significant Weight Loss: BPD surgery has been shown to result in substantial and sustainable weight loss. This is due to the dual mechanism it employs, which limits both the amount of food that can be consumed and the absorption of nutrients by bypassing a portion of the small intestine.
2. Resolution or Improvement of Obesity-related Health Conditions: Many individuals who undergo BPD experience improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and joint pain. The reduction in excess body weight can lead to better overall health and a higher quality of life.
3. Long-term Results: Unlike other weight-loss procedures, BPD has been proven to offer long-lasting results for many patients. Studies have shown sustained weight loss even after several years post-surgery.
4. Improved Metabolic Function: BPD alters how your body processes food by re-routing the digestive system. This can lead to enhanced metabolic function, including improved insulin sensitivity and hormone regulation.
5. Enhanced Quality of Life: Shedding excess pounds not only improves physical health but also boosts self-esteem and mental well-being. With increased mobility, decreased reliance on medication, and newfound confidence in appearance comes a greater sense of fulfillment.
It’s important to remember that while there are numerous benefits associated with biliopancreatic diversion surgery, it is still a major surgical procedure that carries risks and potential complications.

Risks and Complications Associated with Biliopancreatic Diversion
Risks and complications are an important aspect to consider when it comes to any surgical procedure, including biliopancreatic diversion. While this surgery is highly effective for long-term weight loss, there are potential risks involved that patients should be aware of.
One potential risk is infection at the incision site or inside the abdomen. This can occur in any surgical procedure and may require medical intervention such as antibiotics or drainage if necessary. Another possible complication is bleeding during or after the surgery. In some cases, blood transfusions may be required to address excessive bleeding.
There’s also a risk of leaks or fistulas developing at the points where the intestine has been connected. These openings can lead to infections and other complications that might necessitate further procedures to correct them.
Nutritional deficiencies are another concern with biliopancreatic diversion surgery since it involves rerouting part of the digestive system. Patients may need lifelong supplementation with vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12.
Furthermore, gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea and dumping syndrome (rapid emptying of stomach contents) can occur post-surgery due to changes in digestion and absorption processes.
It’s crucial for individuals considering biliopancreatic diversion surgery to thoroughly discuss these potential risks and complications with their healthcare provider before making a decision.
Who is a Candidate for Biliopancreatic Diversion?
Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD) may be recommended for individuals who are severely obese and have not had success with other weight loss methods. However, it is important to note that BPD is considered a more aggressive form of weight loss surgery and is typically reserved for those with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 50 or those with certain obesity-related health conditions.
Candidates for BPD should also have a strong commitment to making long-term lifestyle changes in order to achieve successful outcomes. This includes adhering to dietary guidelines, exercising regularly, and attending follow-up appointments with their healthcare team.
Additionally, candidates must undergo a thorough evaluation by their healthcare provider to ensure they meet the necessary physical and psychological criteria. This assessment will include medical history review, physical examinations, blood tests, and possibly consultations with specialists such as nutritionists or psychologists.
It’s crucial for potential candidates to understand the risks and benefits associated with BPD before making a decision. The procedure can result in significant weight loss but carries the risk of complications such as malnutrition or vitamin deficiencies. Therefore, open communication between the patient and their healthcare team is essential throughout the entire process.
Remember: each individual’s situation is unique! Consulting with an experienced bariatric surgeon will help determine if BPD is the right option based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Stay tuned for our next blog section where we’ll delve into more details about what happens during the biliopancreatic diversion procedure!
Biliopancreatic Diversion Procedure
The Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD) procedure is a surgical weight loss solution that has shown promising results for long-term weight management. This procedure combines both restrictive and malabsorptive techniques to help patients achieve significant weight loss.
During the BPD procedure, the surgeon creates a smaller stomach pouch by removing a portion of the stomach. This limits the amount of food that can be consumed at one time. Additionally, a bypass is created further down in the intestine to reduce absorption of calories and nutrients.
One advantage of the BPD procedure is its effectiveness in promoting substantial weight loss. Studies have shown that patients who undergo this surgery experience an average excess body weight loss of around 70-80 percent within two years post-surgery.
Another benefit of BPD is its potential impact on improving certain obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. Many patients report significant improvements or even complete resolution of these conditions after undergoing BPD surgery.
Like any surgical procedure, there are risks and complications associated with BPD. These can include infection, bleeding, leaks from staple lines or sutures, vitamin deficiencies, dumping syndrome (rapid emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine), and gallstones.
Candidates for BPD are typically individuals with severe obesity (BMI over 40) or those with a BMI over 35 along with serious obesity-related health conditions. It’s important for candidates to have tried other non-surgical methods of weight loss without success before considering BPD.
The recovery period after BPD surgery varies from person to person but generally involves staying in the hospital for a few days following surgery. Patients will need to follow specific dietary guidelines provided by their healthcare team and gradually reintroduce solid foods over time.
In conclusion,
Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD) is an effective surgical solution for long-term weight loss in individuals who meet certain criteria. This procedure combines both restrictive and malabsorptive techniques to help patients

