Muscular Dystrophy Treatment
Can stem cells regrow muscle?
When the cells in your muscle become injured, they send out biochemical signals via your endocrine system. Stem cells respond to those signals, rushing to the injured area and releasing proteins that nourish and stimulate your cells to begin regenerating.
STEM CELL THERAPY FOR MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
Stem cell treatment for muscular dystrophy has shown the highest potential for success and improving the quality of life.Stem cells are defined by certain features and, foremost, an ability for long-term self-renewal and the capacity to differentiate into multiple cell lineages. The growth and preservation of tissues and organs are managed by stem cells.
Stem cell therapy for muscular dystrophy uses two approaches , one that uses bone-marrow derived autologous cells that are altered in vitro to produce dystrophin secreting cells and other being allogenic umbilical cord mesenchymal cells with functional dystrophin.
This method has given promising results as there is progressive transmission of muscle proteins ,making it the best muscular dystrophy treatment in India.
Major Role of cell therapy for Muscular Dystrophy :
- Paracrine or secretory function that has an anti-inflammatory action
- Repair of muscle protein by myogenic progenitor cells
- Bone marrow-derived cells have Anti-apoptotic property
- Strengthening of the neuromuscular junction
- Angiogenesis
If you or a loved one are living with Muscular Dystrophy, time is of the essence! This condition is progressive and can lead to a significant decline in muscle strength and function, impacting daily activities and quality of life. It’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to receive the most effective treatment options available. Don’t delay – take action now to manage your condition and preserve your physical abilities with stem cell treatment for muscular dystrophy in India.
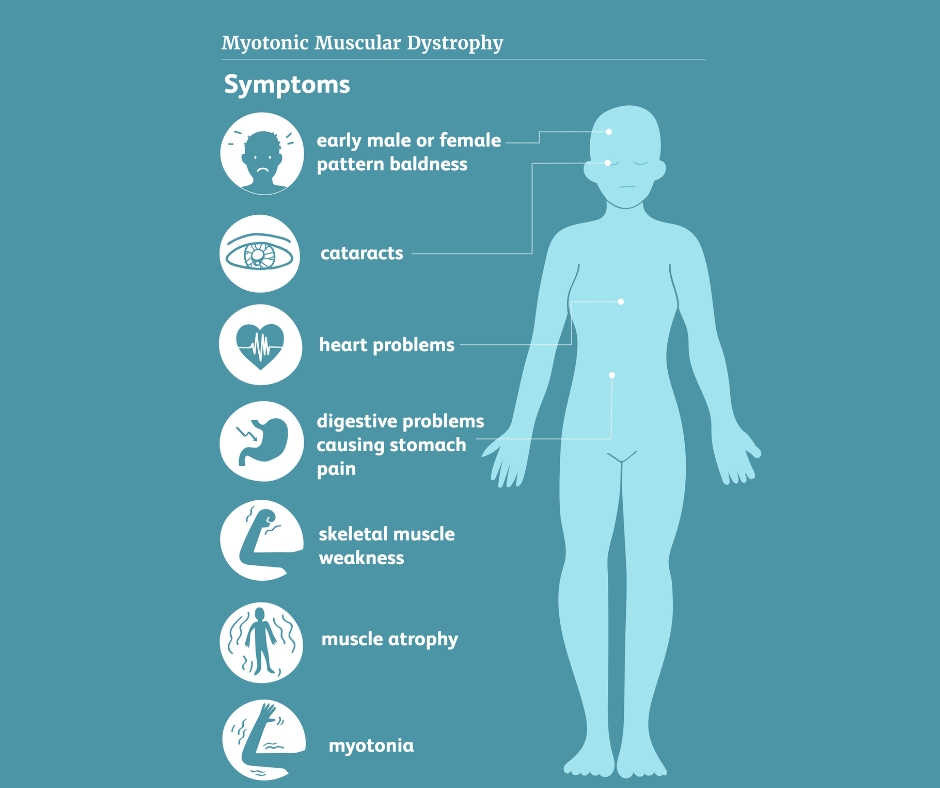
WHAT IS MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY?
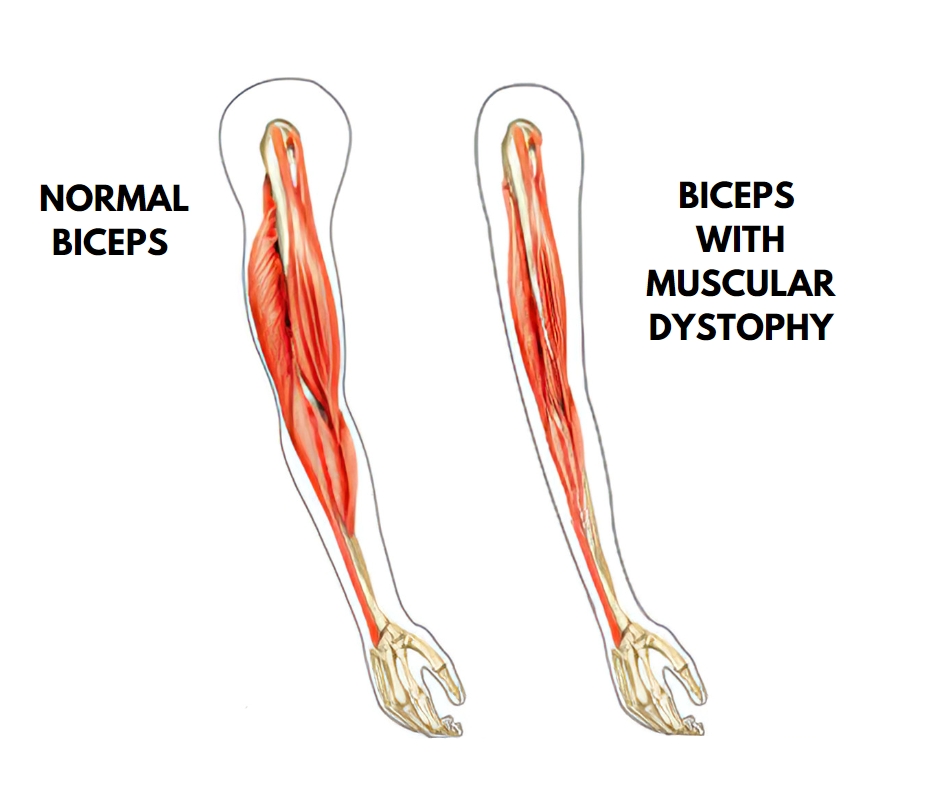
Muscular dystrophy is a heterogenous group of inherited disorders recognized by progressive degenerative muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue(begins in early childhood). There are defects in the muscle proteins and death of muscle cells and tissue.
Regenerative medicine and neurorehabilitation has great potential for Muscular Dystrophy treatment in India.
Specification :
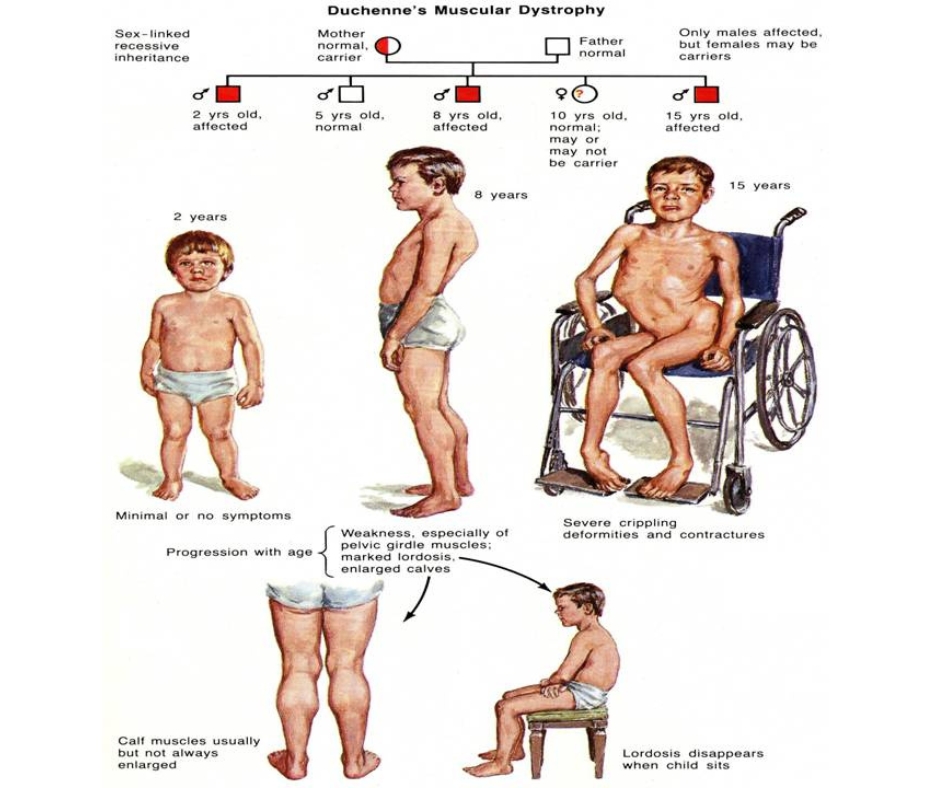
- Occurs primarily in males and rarely in females as it is has a X-linked recessive inheritance
- Most commonly seen
Age of Onset : 2-5 years
Causes : The major cause of Duchenne muscular dystrophy is the malfunctioning of one or more genes, making it a genetic disorder.
Symptoms :
- Calf muscle hypertrophy
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cognitive impairment
- Delayed speech
- flexion contraction
- waddling gait
- global developmental delay
- Retarded motor delay
- Progressive muscle weakness
- Respiratory insufficiency
Specification :
- X-linked inheritance but milder than DMD
- Occurs in both males and females
Age of Onset : 11-25 years
Causes : Genetic mutation and hence wrong expression of the gene
Symptoms :
- Difficulty in climbing the stairs and walking
- Exercise intolerance
- Myalgia
- Lower limb deformity
- Abnormal liver function
- Fatigue and muscle spasm
- Tip-Toe gait
Age of Onset : At birth or early infancy
Causes :The proteins that are essential for the proper functioning of muscles, and in some cases, the eyes and brain, are impacted by genetic mutations, leading to the development of CMD.
Symptoms :
- Progressive muscle weakness initially identified as hypotonia
- Delayed motor milestones like rolling over,sitting up or walking. In some cases milestones might not be met.
- Deformed spinal curvature
- Respiratory deficit
- Learning disabilities
- Seizures and vision problems
Specification :Inherited in Autosomal dominant pattern
Age of Onset :Adolescent to middle age
Causes : There are two types :
- LGMD1 caused due to Autosomal dominant inheritance
- LGMD2 caused to Autosomal recessive inheritance
Symptoms :
- The unifying features of LGMD are the weakness and atrophy of the voluntary limb-girdle muscles
- Waddling gait
- In few cases cardiomyopathy and cardiac arrhythmias is noticed
Specification : Third most common type of muscular dystrophy
Age of Onset : Before the age of 20
Causes : FSHD 1 and FSHD2 are caused by genetic mutations or faulty expressions of some genes.
Symptoms : Muscles of the face, shoulder blades and upper arms are most affected
Specification :Muscles shrink and hence appear atrophied. Poor grip and functional loss of the muscle mass
Age of Onset : 40-60 years
Causes : The mutation of at least eight genes that play a crucial role in muscle function leads to DD. This disorder can be inherited either in an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern.
Symptoms :
- Distal myopathy with vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness
- Finnish (tibial) distal myopathy- Muscle weakness of digital muscles
- Gowers-Laing distal myopathy
- Hereditary inclusion-body myositis type 1 – Foot drop
- Miyoshi distal myopathy
- Nonaka distal myopathy
- Welander’s distal myopathy;
Specification : Rare genetic condition affecting the muscles of the upper eyelid and throat (pharynx particularly) Autosomal dominant form
Age of Onset : 40-50 years of age
Causes : The PABPN1 gene’s genetic defect is responsible for OPMD, as it causes the creation of a dysfunctional protein that clusters in muscle cells.
Symptoms :
- Drooping eyelids or ptosis
- Difficulty in swallowing or dysphagia
- Weakness of tongue
- Limitation in upper gaze
- Weakness in proximal muscles
- Facial muscle weakness
Specification : A collection of genetic, progressive conditions that mainly impact voluntary muscles.It also affects the cardiac muscles.
Age of Onset :By the age of 10
Causes : EDMD occurs due to genetic mutations in the genes responsible for producing proteins that make up the membrane encircling the nucleus of each muscle cell. X linked inheritance is noticed
Symptoms :
- Toe walking due to stiff Achilles tendon of the heel
- Joint stiffening may cause limitation in the arm,neck and spine movements.
- Conduction block is a common feature.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS FOR MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY:
1. Enzyme Test: CPK levels are tested as their presence indicates traumatic injury .
2. Genetic Testing: To give a confirmatory diagnosis for gene mutation
3. Muscle biopsy: It helps to differentiate between muscle dystrophy and other muscle diseases.
4. Heart and Lung monitoring tests: To check for heart and lung function.
5. Electromyography:Changes in the pattern of electrical activity can confirm a muscle disease.
Let Our Patient Speak For Us
my name is Harpreet Kaur age 26 Years Came from Punjab and i am Suffered from Muscular Dystrophy. I had no power in her lower part Body . I had difficulty in Sitting for a long time.
My parents heard about the Rehabilitation treatment . i took treatment under Dr.Anant Bagul Sir. After the treatment I have Started gaining muscle power day by Day . I would Sit for Short periods comfortably and also stand.” I am very happy. thank You Universal hospital Doctor & Team.
“Harpreet was very happy with the treatment. She and her parents thanked.
Everyone in Universal Hospital and Said that she could recommend other patients

Muscular Dystrophy
My Name Is Laxmi Shweta i am 13 yrs old Girl Staying at Small Place in Tamil-Nadu i had extensive Weakness & having paralysis in both upper limb & Lower Limb due to LGMD. after losing all hope my parent Decided to under take a stem-cell Treatment by Dr. Anant Bagul.
It has been Six Month now i am Feeling much Better than Previously. now i don’t Need any Support in walking also get a in my leg And hands. i called helpline no 9011111222 & they Offered lost of support Whenever we needed thanks to Dr Bagul Sir & Hospital

LGMD
Condition before the treatment:
Dinesh suffering from muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a genetic disorder.He had difficulty in walking,due to progressive weakness in all limbs.His CPK level was more than 20,000IU.His parents knows the prognosis of disease so willing to undergo stem cell therapy.
Condition after the treatment:
There was remarkable improvement in power of both limbs His cpk level reduced upto 1000 IU in three months. His gait pattern also improved.

Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Frequently Asked Questions...
Stem cells are a valuable tool in muscular dystrophy research in two ways: by acting as models for the disease, and in their role as a direct treatment for the condition.

