Neurology & Neurosurgery

Neurology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the nervous system, which includes the:
-
Central nervous system (CNS): the brain and spinal cord
-
Peripheral nervous system (PNS): nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord
-
Autonomic nervous system (ANS): controls involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion

Key Areas in Neurology
-
Headache Disorders
-
Migraines, tension headaches, cluster headaches
-
-
Epilepsy
-
Seizure disorders caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain
-
-
Cerebrovascular Diseases
-
Stroke, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
-
-
Movement Disorders
-
Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia
-
-
Neurodegenerative Diseases
-
Alzheimer’s disease, ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease), Huntington’s disease
-
-
Multiple Sclerosis and Demyelinating Disorders
-
Neuromuscular Disorders
-
Myasthenia gravis, peripheral neuropathy
-
-
Infections and Inflammatory Diseases
-
Meningitis, encephalitis, autoimmune encephalopathies
-
-
Sleep Disorders
-
Narcolepsy, restless legs syndrome, insomnia (neurological causes)
-
-
Brain and Spinal Cord Injuries
-
From trauma or disease processes
-
Diagnostic Tools in Neurology
-
MRI and CT scans – Imaging to view brain/spine structure
-
EEG (Electroencephalogram) – Measures brain wave activity
-
EMG/NCS (Electromyography & Nerve Conduction Studies) – Tests nerve and muscle function
-
Lumbar Puncture – Analyzes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Neurologist vs. Neurosurgeon
-
A neurologist is a medical doctor who diagnoses and treats neurological disorders using medications and non-surgical methods.
-
A neurosurgeon is a surgical specialist who operates on the brain, spine, and nervous System
Neurosurgery In India
Neurosurgery is a specialized field of surgery that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and surgical intervention of disorders related to the nervous system. This includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Key Areas in Neurosurgery
-
Brain Surgery
-
Tumors: Removal of brain tumors, whether benign or malignant.
-
Trauma: Surgery to repair brain injuries caused by accidents or falls.
-
Aneurysms: Surgical repair of brain aneurysms to prevent rupture.
-
Epilepsy: Surgery to treat severe, drug-resistant epilepsy by removing brain tissue that causes seizures.
-
Hydrocephalus: Surgery to treat fluid buildup in the brain through a procedure called a shunt placement.
-
-
Spinal Surgery
-
Disc Herniation: Removing or repairing herniated discs that press on nerves.
-
Spinal Deformities: Surgery to correct spinal deformities like scoliosis.
-
Spinal Cord Injury: Surgical treatment of traumatic injuries to the spinal cord, often focusing on stabilizing the spine and decompressing nerve structures.
-
Spinal Tumors: Removal of tumors from the spinal column or spinal cord
-
-
Peripheral Nerve Surgery
-
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Surgical decompression of the median nerve in the wrist.
-
Nerve Repair: Surgery to repair damaged nerves, especially in cases of trauma, to restore function.
-
-
Functional Neurosurgery
-
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Involves implanting electrodes in the brain to treat conditions like Parkinson’s disease, tremors, and other movement disorders.
-
Pain Management: Procedures to relieve chronic pain through spinal cord stimulation or other interventions.
-
-
Endoscopic and Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery
-
These techniques use smaller incisions, advanced imaging, and specialized instruments to minimize damage to surrounding tissues and promote faster recovery.
-
Commonly used in brain tumor surgeries, spinal surgeries, and some types of brain aneurysm repairs.
-
-
Vascular Neurosurgery
-
Aneurysm Clipping or Coiling: Surgery to treat brain aneurysms (weak areas in blood vessels).
-
Carotid Endarterectomy: Removal of plaque from the carotid artery to prevent strokes.
-
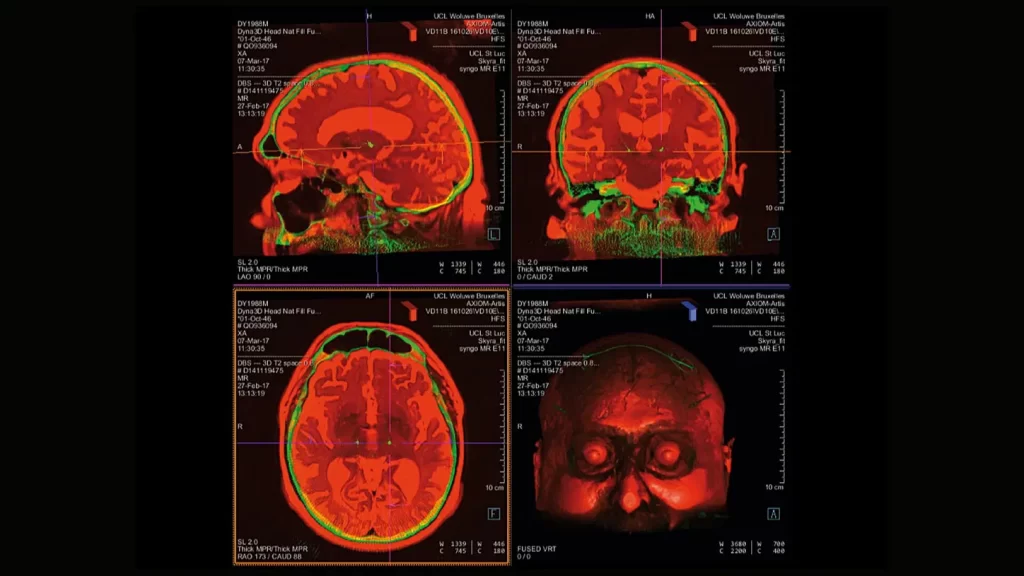
Neurosurgical Technologies
-
Robotics: Increasingly used for precision in surgeries, such as in minimally invasive spinal procedures.
-
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: A non-invasive procedure for treating brain tumors or arteriovenous malformations using targeted radiation.
-
Endoscopes: Thin tubes with cameras that allow neurosurgeons to perform minimally invasive surgeries.
Neurosurgery vs. Neurology
-
Neurologists primarily focus on diagnosing and treating neurological conditions with medications and non-invasive techniques. They don’t perform surgeries.
-
Neurosurgeons are trained to perform surgery to treat neurological conditions, including brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerve disorders.
Key Surgical Procedures in Neurosurgery
-
Craniotomy: Opening the skull to access the brain. This is often done to remove tumors, treat brain injuries, or repair aneurysms.
-
Laminectomy: Removal of part of the vertebra (lamina) to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
-
Spinal Fusion: Fusing two or more vertebrae to prevent movement and stabilize the spine.
-
Microsurgery: Involves using high magnification to perform delicate surgeries, often to remove small tumors or repair tiny blood vessels.
Diagnostic and Pre-Surgical Tools
-
Neuroimaging (MRI, CT scans, PET scans): Provides detailed images of the brain and spine to help guide surgery.
-
Intraoperative Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of brain or spinal cord activity during surgery to prevent damage to critical functions.
-
Stereotactic Surgery: Uses 3D imaging to pinpoint precise locations in the brain for treatment, often used in deep brain stimulation or tumor removal.
Common Conditions Treated by Neurosurgeons
-
Brain Tumors: Benign or malignant growths in the brain.
-
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Brain damage due to external injury.
-
Cerebral Aneurysms: Weakened areas in the brain’s blood vessels that may rupture.
-
Spinal Cord Injury: Damage to the spinal cord, which may lead to paralysis or loss of sensation.
-
Degenerative Spine Conditions: Such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis.
-
Movement Disorders: Such as Parkinson’s disease, for which surgical options like deep brain stimulation (DBS) may be used.

