Paediatric Orthopaedics

Paediatric orthopaedics is the branch of medicine that deals with injuries and musculoskeletal conditions in children and teens.
It is also sometimes known as paediatric orthopaedic surgery. The most common issues that children experience are foot deformities, gait disturbances, and hip dysplasia, among others.
Pediatric Orthopedic Conditions
Children face various orthopedic challenges, and some of the most common conditions treated at our hospital include:
- Foot Deformities: Issues like clubfoot, flat feet, or other deformities that affect the shape and function of a child’s feet.
- Gait Disturbances: Problems such as limping, toe-walking, or uneven walking patterns caused by muscle or joint issues.
- Hip Dysplasia: A condition where the hip joint doesn’t form properly, leading to instability or dislocation.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal curvature of the spine, often detected during growth spurts.
- Fractures and Sports Injuries: Broken bones or injuries resulting from falls, accidents, or active sports.
- Congenital Limb Deformities: Birth defects or abnormalities that affect the limbs and may require surgical intervention or physical therapy.
Common Conditions Treated in Pediatric Orthopaedics:
Congenital conditions:
Clubfoot
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
Limb length discrepancies
Trauma and fractures:
Growth plate fractures
Elbow fractures (e.g., supracondylar humerus)
Spinal conditions:
Scoliosis
Kyphosis
Neuromuscular disorders:
Cerebral palsy-related deformities
Muscular dystrophy
Infections and tumors:
Osteomyelitis
Bone cysts or benign tumors
Gait abnormalities:
Toe walking
In-toeing and out-toeing
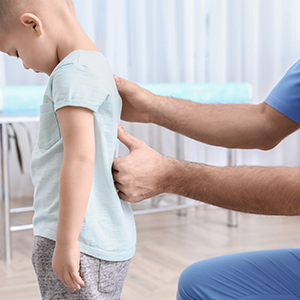
Differences from Adult Orthopaedics:
Children’s bones are still developing, allowing for greater remodeling potential.
Many conditions are unique to childhood or are growth-related.
Treatments often emphasize non-surgical management when possible (e.g., casting for clubfoot).
Pediatric orthopaedic surgeons must consider future growth when planning treatments or surgeries

